Na-19 Franck-Hertz Experiment
AIM
To demonstrate the quantum nature of atoms by electrons being absorbed into Mercury atoms.
APPARATUS
- Franck-Hertz Apparatus
- Control Unit
- Oscilloscope

DESCRIPTION
The purpose of this demonstration is to illustrate how atoms absorb electrons at a quantized energy level using the Franck-Hertz Experiment.
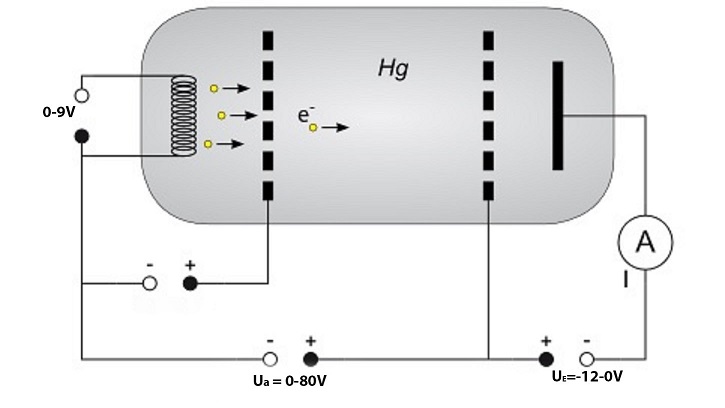
Refer to above diagram. In an evacuated tube with a small amount of Mercury. First the tube is heated to 180℃ to make the Mercury into a gaseous state. Electrons are produced by a filament and then accelerated with a small voltage towards an electrode grid. Then the electrons are accelerated towards the anode grid with a voltage range 0-80V. The electrons are then deaccelerated with a small voltage range -12-0V, so that electrons with an above energy threshold will reach the collector plate. The current is measured by some circuitry.
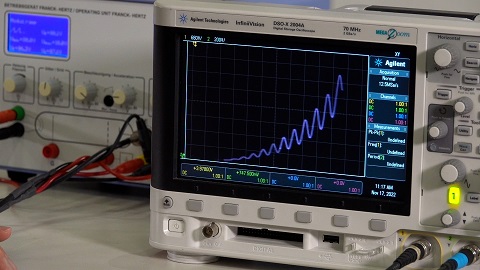
The voltage of the anode grid and current of the collector plate are connect to an Oscilloscope for analysis. The control unit of the Franck-Hertz apparatus will sweep the anode voltage from 0V to the set voltage with a maximum of 80V. It is observed that the current will increase with voltage until a voltage of 4.9V is reached. The current dramatically decreases when this voltage is reached. As the anode voltage is further increased the current will start to increase again until a voltage of 9.8V, where the current will dramatically decrease again. The process is repeated in steps of 4.9V. to maximum anode voltage of 80V. First, we consider the voltage range of 0-4.9V. The electrons are accelerated toward the anode grid. The electrons will collide with Mercury atoms and have elastic collisions. Only electrons that have an energy of 4.9eV will lose most their energy in the collision with Mercury atoms. That is an inelastic collision. Causing an electron within the Mercury to be excited into a higher energy level. The electron will then return to its original energy level, thus emitting a photon of 254nm in the Ultraviolet range. Most of these inelastic collision will happen near the grid where the voltage is 4.9V.
When the anode voltage is 9.8V. Electrons that have been accelerated to the midway point between the electrodes will gain an energy of 4.9eV. Where inelastic collision will occur. Electrons that have lost most of their energy after inelastic in the midway point. Will be accelerated towards the anode grid and gain 4.9eV near the grid. Therefore, capable of having another inelastic collision. Thus, another dramatic decrease in current when the anode voltage of 9.8V.
The process is repeated in further steps 4.9V of increase of anode voltage.
This experiment demonstrates the quantum nature of electron energy levels in atoms.